What Is 3D Metal Printing?
by Mike
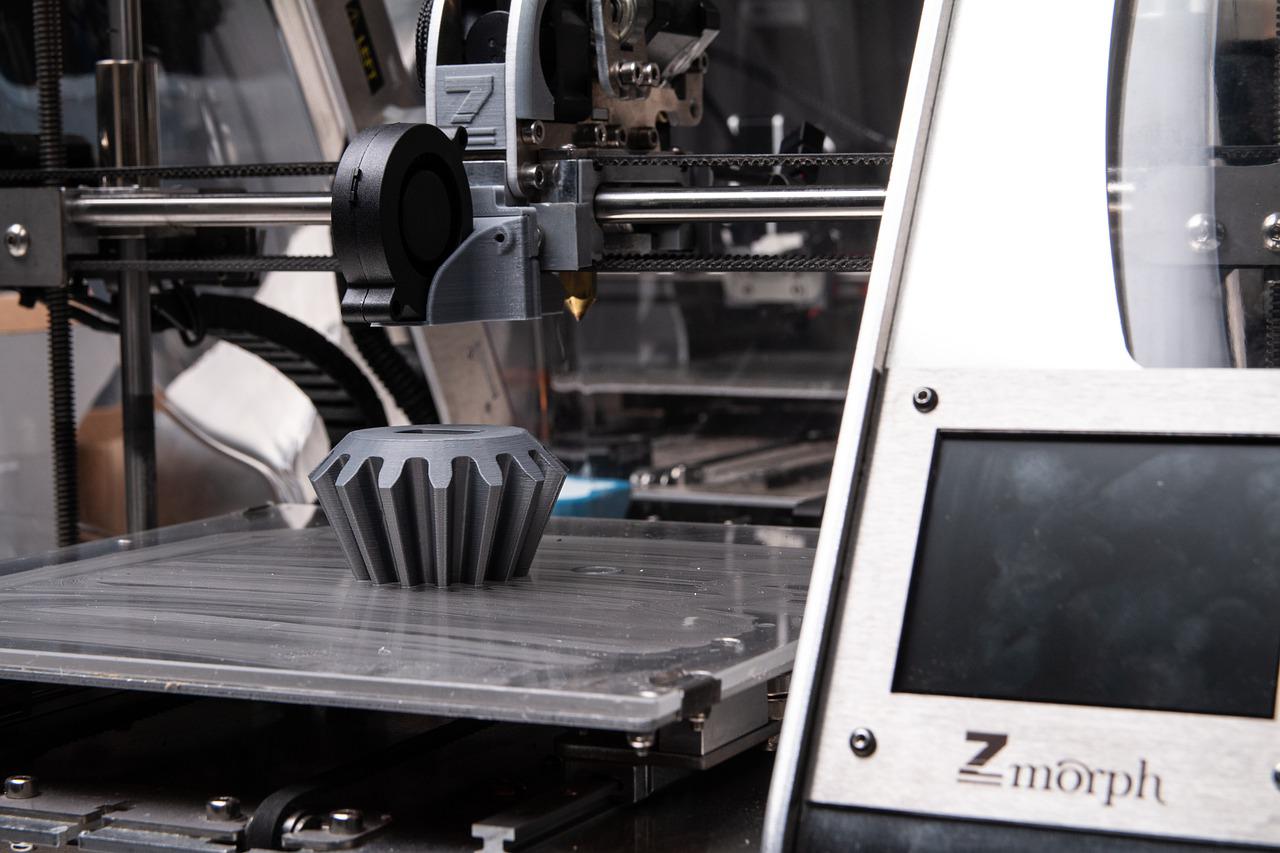

How does 3D metal printing work? 3D metal printing is one of the newest and most exciting forms of manufacturing. It’s a fairly new technology that has proven to be very useful in many different industries, including art and manufacturing. Digital fabrication creates solid physical objects from digital files. It may be a bit odd to think of 3D printing as manufacturing, even though that is what it is. But after I explain how this technology is used to make metal objects, you will realize that it is possible because of various physical properties of metals that are manipulated by an additive manufacturing process like 3D printing.
What is it?

The easiest way to describe metal 3D printing is the process of taking a computer-assisted design (CAD) file and transforming it into a real, incredibly accurate physical part.
The technology works by slicing the CAD model into thin horizontal layers, and piling them on top of one another.
How the process goes
Essentially, when you zoom in, 3D metal printing is a process where metal is melted and then deposited in layers to create a three-dimensional object. The process of 3D metal printing involves melting a pool of metal powder and fusing it together with a laser or electron beam. This process can be used to create any shape imaginable, including molds for casting. 3D metal printing originated in the 1980s, when MIT researchers developed a method of computer-controlled machining known as selective laser sintering (SLS). SLS uses a powder bed that is selectively fused by a laser that moves around the bed in three dimensions. The resulting object has poor mechanical properties because there are many gaps between each layer of material; however, this technique paved the way for more advanced techniques such as selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM).
How do CAD designs fit into all of this?

The process of 3D metal printing starts with the computer-aided design (CAD) file of the object to be printed. A layer of powder is spread onto the build platform—this is where the object will be built up. The laser is then fired at the powder, which melts it into a solid form. The laser then moves on to the next layer of powder and repeats this process until the entire object has been built up in layers.
What types of printers are there?
There are two major types of 3D metal printers: selective laser sintering (SLS) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Both use lasers to create objects from powdered metals such as steel or titanium. SLS machines use two-dimensional patterns that are layered on top of each other until they form an object with depth. The layers are built up as liquid resin is solidified by the laser beam before being melted away again. This process is repeated over and over until an entire object is formed. DMLS machines use three-dimensional models instead of two-dimensional ones like SLS models do, which allows them to create more complex shapes than SLS machines can build.
How does 3D metal printing work? 3D metal printing is one of the newest and most exciting forms of manufacturing. It’s a fairly new technology that has proven to be very useful in many different industries, including art and manufacturing. Digital fabrication creates solid physical objects from digital files. It…